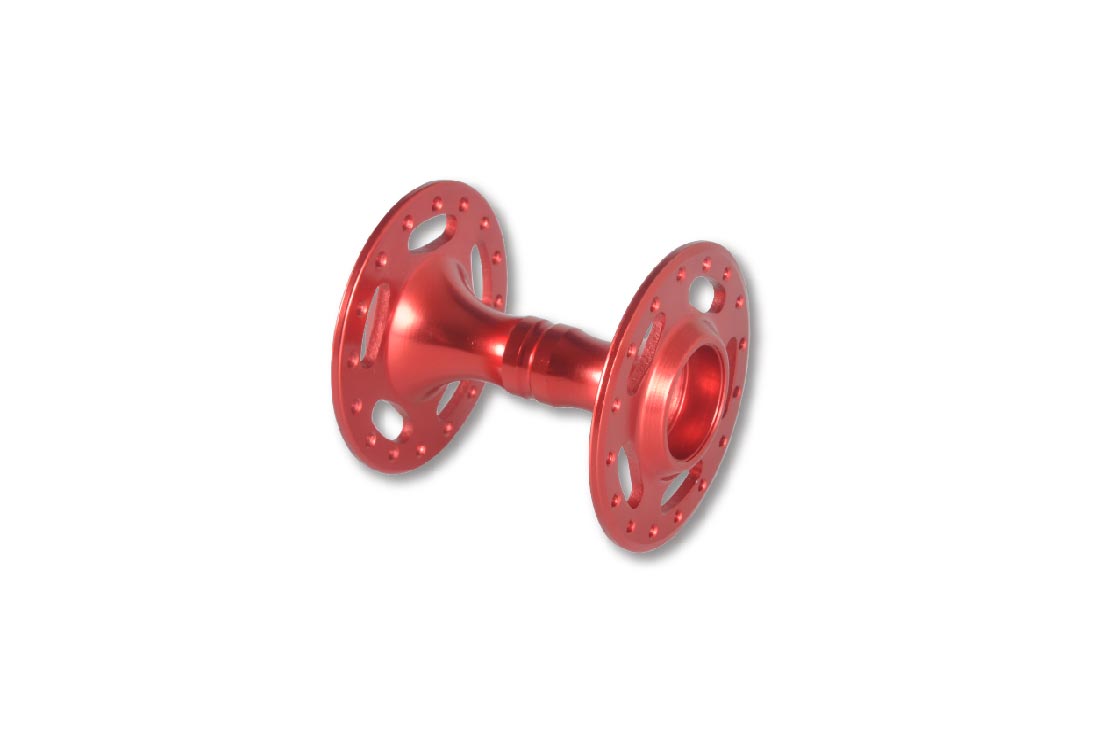
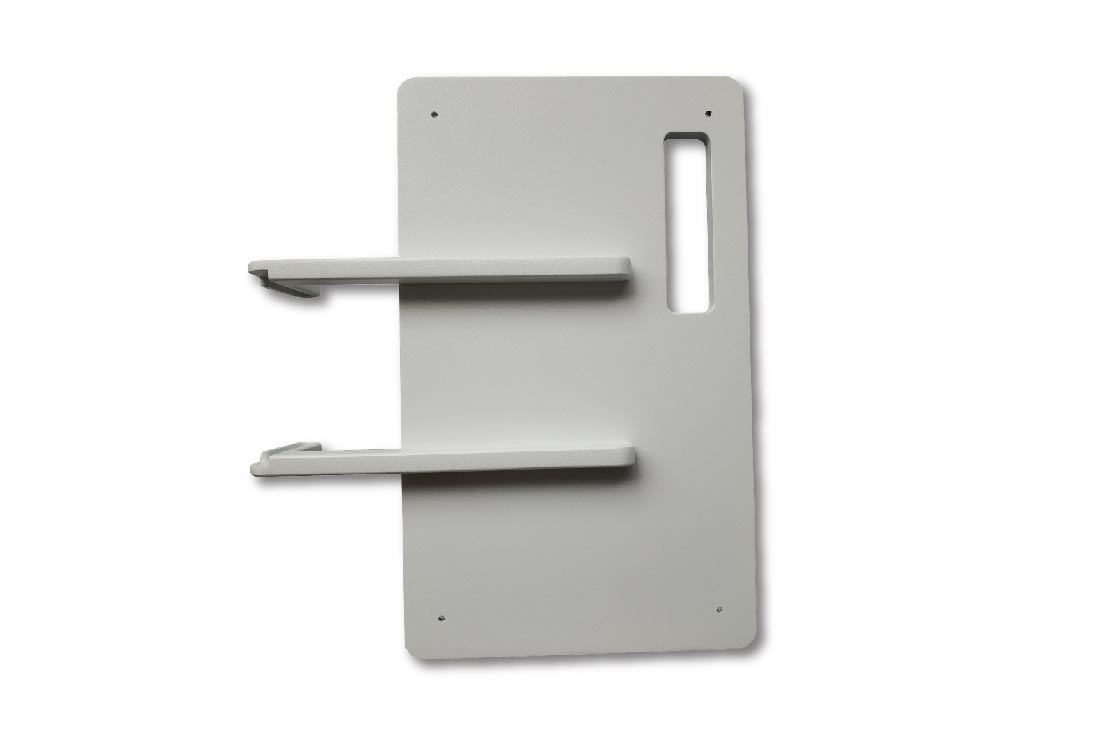
Your Finest Product Prototype Manufacturer in China
At Sunrise Metal, product prototype service is one of the full set manufacturing services. Sunrise Metal’s high accuracy manufacturing machines—5 axis and 7 axis CNC machines and advanced measurement instruments—Carl Zeiss CMM, etc, can guarantee the quality of your product prototype projects.
At Sunrise Metal, we are not only offering you product prototypes, but also DFM. The suggestions we raise about how to short production time and reduce the cost based on no discount parts’ quality. You also can https://www.sunrise-metal.com/product-prototype/find the benefit of our Product prototype CNC machining services with our many kinds of surface treatments, from normally surtec650 or chromate to liquid painting or plating.
And we think what you think. The Shortest lead time and the competitive cost is our promise to succeed in your product prototype business. Looking learn more about aluminum die casting.
Sunrise Metal, Rich Experienced Manufacturer for Your Product Prototype Parts
A Good product prototype is a visual sample in your product development process. It can provide engineers or the creator a physical part to see their idea come to life. The Product prototype can not only realize your idea or concept but also can help you greatly optimize your design and give you a most comprehensive feasibility analysis with a real sample. So as to a good Product Prototype supplier, Sunrise Metal’s CNC machined Product prototype can save your cost and project lead time, rather than to make a pilot or soft tool–for whatever your plastic or aluminum or other metal parts.
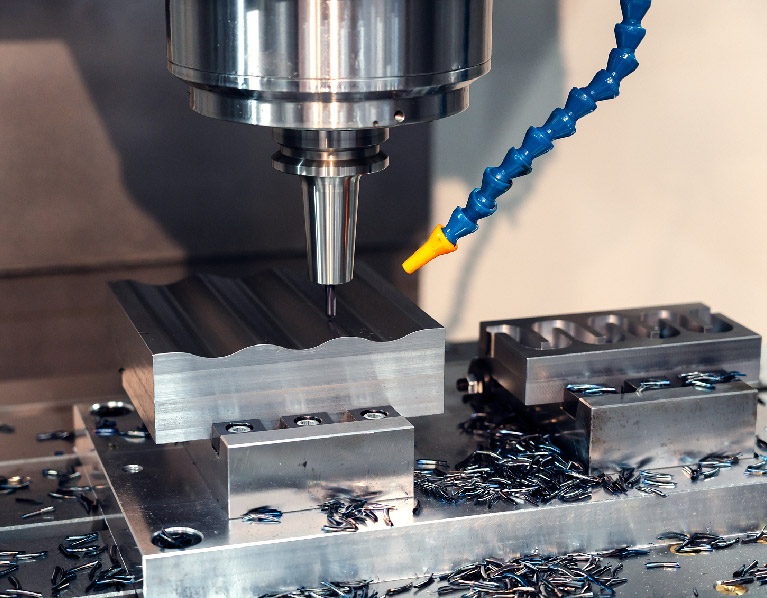
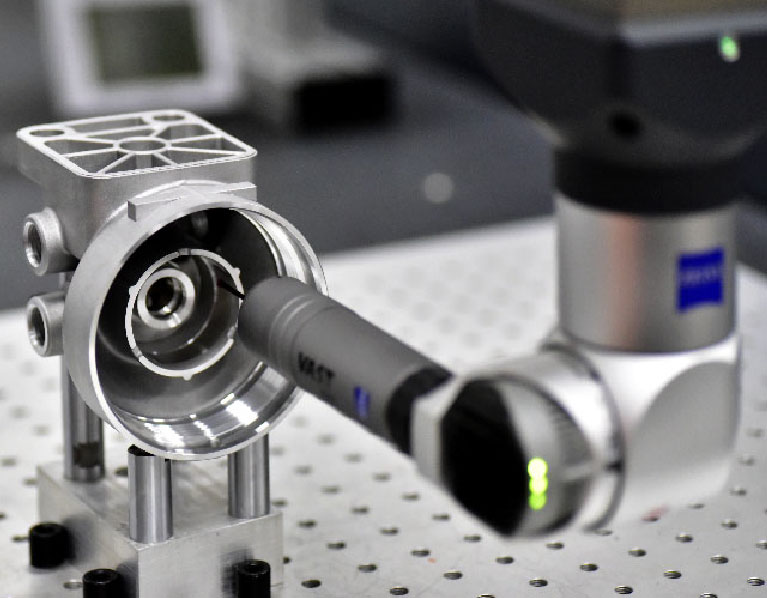

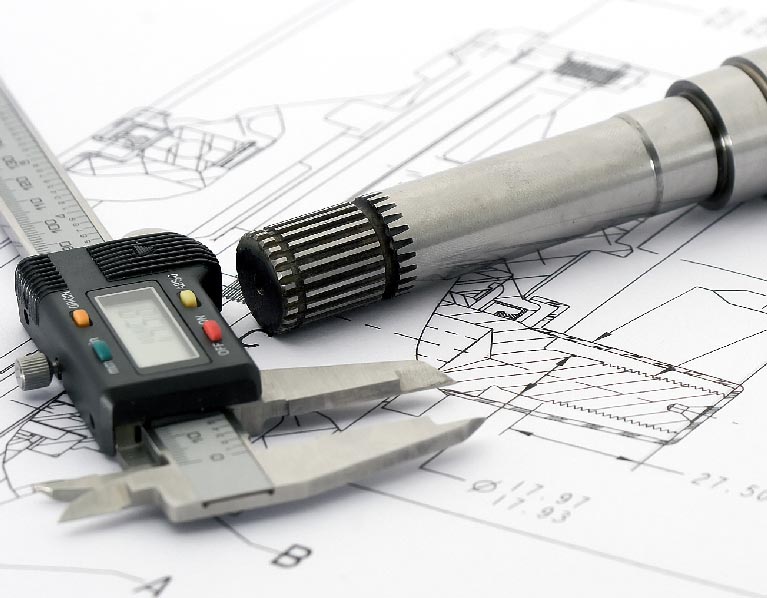




Advanced Machining and Measurement Equipment For Your Product Prototype Projects
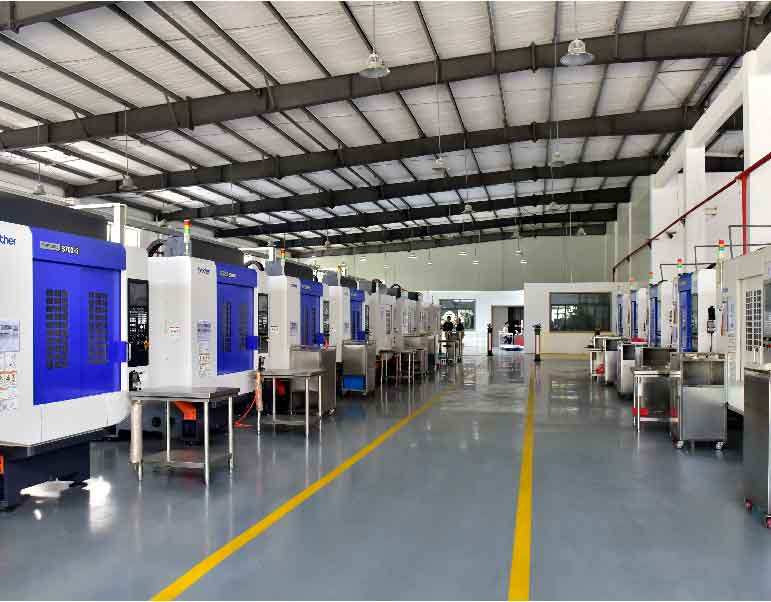
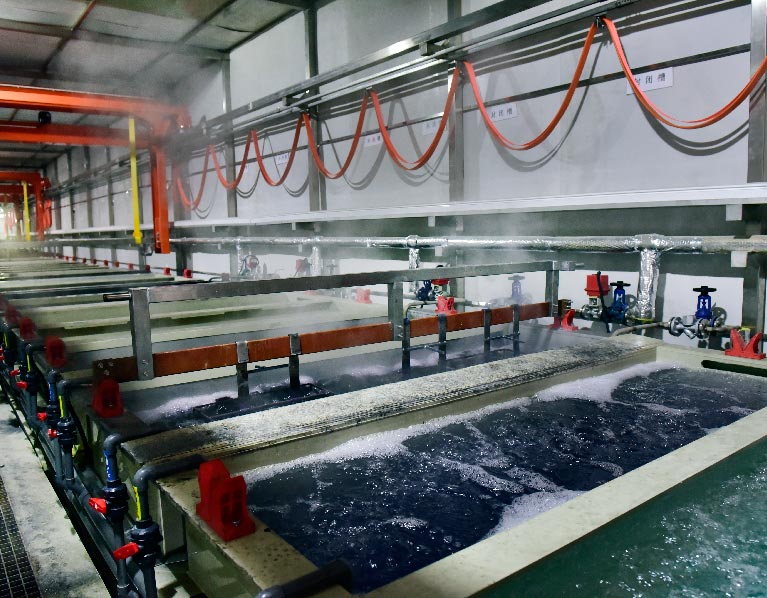
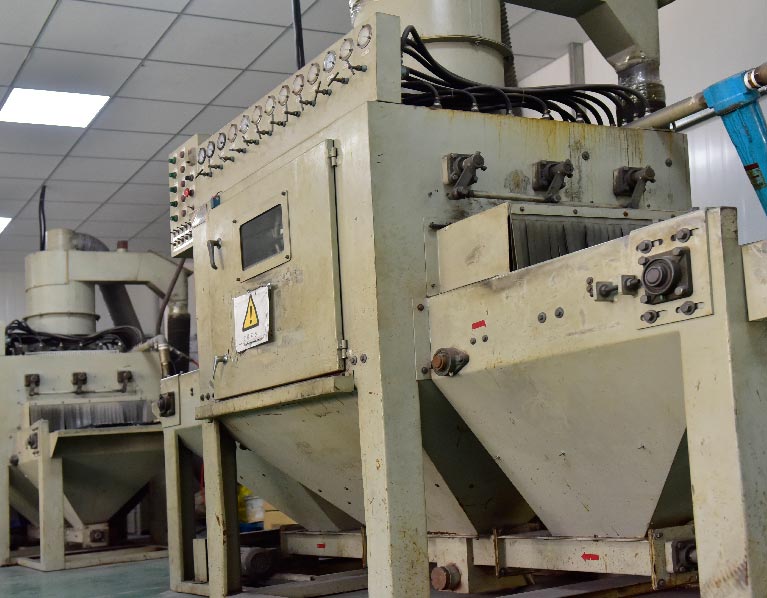




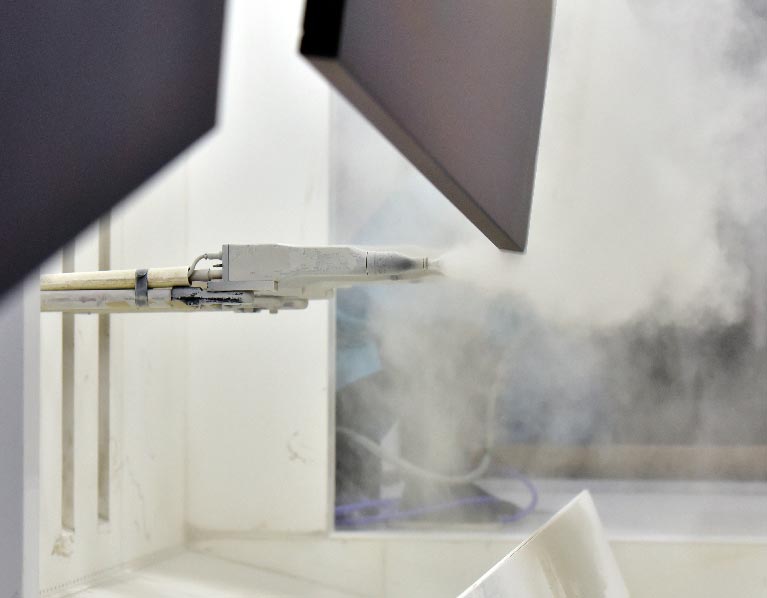

Recent Product Prototype Projects Sunrise Metal Ever Made

Part Name: HEAT SINK OF CIRCUIT BOARD
Material: AlSi12
Size: 355x283x29 mm
Weight: 1665g
Machine Tonnage: 500T
Surface Finish: Chromating
Production Process: Die Casting–Trimming–Deburring
–CNC Machining–Chromating–Screening–Packaging
Applied Industry: Medical
Part Name: lAMP MOUNTING BASE
Material: ADC12
Size: 551*416*70 mm
Weight: 1480g
Machine Tonnage: 800T
Surface Finish: Powder Coating
Production Process: Die Casting–Trimming–Deburring
–CNC Machining–Chromating–Coating–Screening–Packaging
Applied Industry: Medical
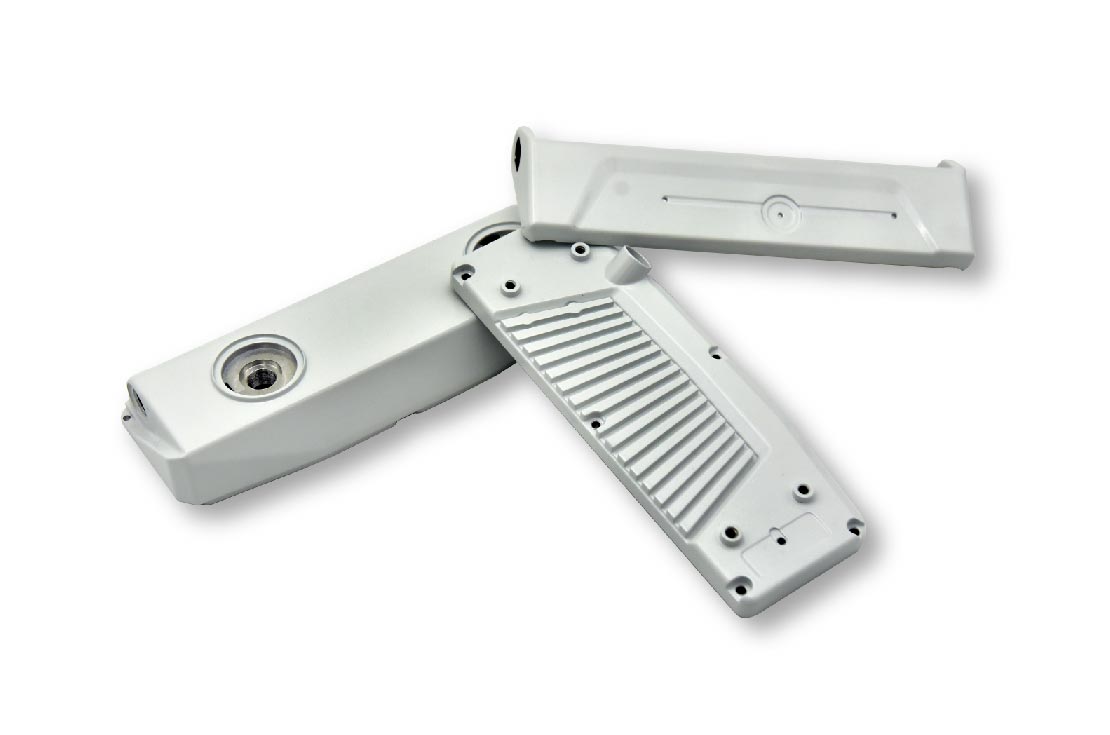

Part Name: HAND SHANK
Material: AlSi12
Size: 357x222x44 mm
Weight: 773g
Machine Tonnage: 500T
Surface Finish: Chromating
Production Process: Die Casting–Trimming–Deburring
–CNC Machining–Assenbly–Powder Coating–Liquid Painting–Screening–Packaging
Applied Industry: Medical

Part Name: MEDICAL BRACKET
Material: AlSi12
Size: 412x46x36 mm
Weight: 182g
Machine Tonnage: 400T
Surface Finish: Chromating
Production Process: Die Casting–Trimming–Deburring
–CNC Machining–Powder Coating–Screening–Packaging
Applied Industry: Medical
PRODUCT PROTOTYPE: THE ULTIMATE FAQ GUIDE
A prototype is used to create a sample of the finished product helping brands build a fully functional product from an initial idea. This article explores what it really means to prototype a product when prototyping should start and the best practices to get the best out of your product prototype.
- What is a product prototype?
- What is the purpose of a product prototype?
- What makes a good product prototype?
- What is the next step after the product prototype?
- How do you make a product prototype?
- What are the types of product prototypes?
- What are the three phases of product prototyping?
- How do I find a manufacturer for my product prototype?
- How much does it cost to prototype a product?
- What are the differences in creating a prototype vs. a final product?
- What are the benefits of product prototypes?
- What is a low fidelity prototype and high fidelity prototype?
- What is the difference between wireframe, mockup, and prototype?
- What is the difference between MVP and product prototype?
- What are product prototype assembly, adjustment, and finishing in manufacturing?
- What are product prototype testing and design evaluation in manufacturing?
- What are the Best Practices for making A Product Prototype?
- What are the differences between a homemade sample and an engineered product prototype?
- Will my prototype be as good as a finished product?
- What is the typical timeframe for prototype development?
- What should I consider before choosing a manufacturer for my product prototype?
What is a product prototype?
The product prototype is a rough working sample or mockup of the actual product based on which the final product is created. When designing a product, there are a lot of considerations to make and decisions to be made. Without a working sample, you cannot approach investors to get the capital needed for the actual inventory, for example.
You might also need this simulation of the real product to see if it is viable for mass production. Having a prototype isn’t simply a part of the creation process, it is an important part of the startup process that helps build future products. Think of it as a roadmap to the direction that the company is taking with the end goal as the final functional product ready to hit the shelves.
Prototyping is meant to take the design process to the next step in manufacturing. It is difficult to call it prototyping if you have gone through the process without getting a deeper understanding of your product and how best to manufacture it.
What is the purpose of a product prototype?
As mentioned above, having a product prototype is integral in displaying and explaining your idea to investors. How would an investor tell if they want to invest in your company if you have no sample to show for your idea? The main aim of having a product prototype is to validate your design.
A startup may also need to raise capital through crowdfunding, and having a product prototype is crucial in demonstrating the idea to potential investors. Some crowdfunding companies have strict requirements like Kickstarter which demands product campaigns to be accompanied by a prototype.
Another reason why it is vital to have a prototype is for intellectual property protection. It helps to have your idea in solid form proving that indeed you are the owner of the product.
Top reasons for a product prototype;
- Safeguarding intellectual property rights
- Showcasing your product idea in action
- To help show areas that may need improvements after design
- To demonstrate the product to potential investors and clients
- To test the product to see if it works
- To avoid manufacturing errors and costly amendments later on
What makes a good product prototype?
There isn’t a one shoe fits all in prototyping to check if a product prototype is good or not. However, there is an idea on what a good prototype should look like.
Here are the top things to aim for in designing a good prototype;
- It should clearly illustrate the true functionality of the real product even if this will be fine-tuned later
- It should look like the end product or at least give a rough idea of how that end product will look like
- It shows how it fits into other components or parts if it part of a larger product
- Proves that manufacturing can be done
- Helps address issues that were not foreseen and improve on aspects that had not been addressed previously
- Gives confidence that the product can move forward to the next stage
What is the next step after the product prototype?
You have created a working prototype and it is just perfect. What next?
Your next step after this is to validate the market. You want to understand your market/end users in a non-biased way. Also, take the time to learn what your vendors need and how you can help them reach their goal.
After this, you should reflect on how you will sell your product and build a brand around it. Do not forget to patent your idea or find another suitable way to protect your ideas from theft. Getting a patent is a crucial part of the process as it grants you exclusive rights to make, use, and sell your own work.
How do you make a product prototype?
There are important considerations to make when making a product prototype. For example, do you have enough funds to make a professional prototype? Do your investors care for a homemade prototype or a manufactured one?
When it comes to making a product prototype, there are several steps to getting the work done.
- Create a concept sketch to have a rough idea of what you desire to create
- Create a virtual prototype. Designers can help you do this if you do not feel competent enough. Get a range of virtual designs that could vary from simple 2D designs to more complicated 3D designs
- Build a physical prototype
- Get a manufacturer
One of the important purposes of having a product prototype is to test the idea. If this is your case, make sure you get feedback from potential users. You should use this feedback to tweak and improve your product until both the users’ needs and wants are met.

What are the types of product prototypes?
A product prototype can take many forms. It could be a digital, 3d, paper, small model, or any other form based on the reasons why it is sought. A functional prototype may not deliver great aesthetics, for example, but will focus on the functionality of the product.
Prototypes can be throwable or permanent depending on their role. Here are the most popular types of product prototype;
- Feasibility prototype – Only developed to determine the technical issues associated with performance, compatibility, and the likes.
- Rapid prototype – Used to promptly engineer a model using a CAD when time is limited
- Horizontal prototype – Used in the early stages, horizontal prototypes show the breadth of the system but do not go deep into the details. They are useful for describing features and a device’s capabilities
- Vertical prototype- Unlike horizontal, vertical prototypes are used in the later stages of the design process. They explain the product features at length and have greater detail even if the product isn’t fine-tuned yet
- Simulations – These are digitally created to predict the feel, look, and performance of a product
- Storyboard – Describes the product in story form using a prepared sequence
- Animations – These are drawn images that are set in a sequence that offers a 3D structure of the final product
- Mock-up – A mock-up is presented to the overall vision of the product. It had no features and is just an estimate
What are the three phases of product prototyping?
We can group phases in product prototyping in three major classifications: Alpha, Beta, and Pilot. Each of these steps has a roadmap and corresponds to a rising score measured against the Technology Readiness Level Scale.
Alpha – Similar to the proof of concept as this step helps you to understand your service.
Beta – This process incorporates the refinements made on the design at the Alpha stage and implements them into production. The software here is fine-tuned.
Pilot – This is the phase when the company rolls out the product to a fraction of the public to see if they will use it. It is a live experiment on how your product performs in the marketplace.
How do I find a manufacturer for my product prototype?
It can be a hard task trying to find a suitable manufacturer for your prototyping needs. When it comes to sourcing products, many entrepreneurs find themselves lagging behind. When choosing a manufacturer, there are important considerations to make. Ask yourself if the manufacturer can meet your needs, do they have experience in the field, and what is the cost of manufacturing.
To get cheaper manufacturing, many companies often look beyond their borders. You may want to source from overseas if the cost of doing so in your home country is hefty. Just be sure that the company you choose can do a stellar job at a good price. Sunrise Metal is a leading manufacturer providing an array of prototyping services. Talk to an expert from the team to get a quotation or free advice.
How much does it cost to prototype a product?
You want to make a good product that will make you money. Making good prototypes can help you design a worthy product while saving you time and money on the wrong moves. By realizing the constraints and needs early enough, you are able to use this to make better products. At the end of the day, it depends on your prototyping needs. There is no given timeline for all kinds of prototypes. Generally, it should take weeks.
What are the differences in creating a prototype vs. a final product?
A prototype is a working sample of the final product. It only focuses on the functionality in a bid to make sure that the prototype is working as the final product should.
The actual product now scores high on other aspects such as quality, performance, user interface, and user experience.
Simply put, a prototype demonstrates how a product will work while an actual product is ready for launch in the market for use. The actual product can withstand stress, load, and other quality aspects.
What are the benefits of product prototypes?
There are several benefits to product prototypes. They include;
Reduced costs and time – Prototyping build on the user experience to offer a final product that has been improved for the market. Good prototypes can help a company save in the long term by avoiding costly amendments and ensuring product quality.
Enhanced user involvement – Most customers appreciate the inclusivity when creating a product for them. Prototyping allows them to feel like they are a part of the process as they interact with a working mockup. With this setup, customers can give feedback, alter model specifications, and request project changes.
Early discovery of design problems – This helps with the elimination of any problematic areas of the design. In the long run, it helps the company save time and money.
It helps the companies and manufacturers figure out the cost of production, manufacturing time, and requirements for materials.
What is a low fidelity prototype and high fidelity prototype?
Two words are often used in prototyping and you may have come across them – high fidelity and low fidelity prototypes. Low fidelity prototypes are mostly based on paper and offer limited user interaction. Also known as lo-fi, product prototyping is a great way to test concepts. These types of prototypes are used to gauge functionality and not aesthetics.
High fidelity prototypes are based on the computer allowing more realistic user interactions as they offer a true representation of the final product. They are better at demonstrating the concept to clients and potential investors.
What is the difference between wireframe, mockup, and prototype?
A sketch is the least lo-fi prototype that uses sketches to explain the concept rather than words.
A wireframe is a basic visual representation of the product. It is a low-fidelity solution to show layouts and structures.
A mockup is a high-fidelity static design diagram that looks like the finished product and shows the functionality of the final product. It is not clickable or interactive but is a graphic representation with content and functions.
All of these represent a different stage of the design flow. It starts with a sketch, wireframe then mockup. Finally, we get the prototype preceding the final fully functional product ready for manufacturing.
What is the difference between MVP and product prototype?
An MVP is a product sample that is between the prototype and the final product. It stands for a minimum viable product and is taken to the market right away. It is ready for use, polished, and without any bugs or issues.
A prototype is made to find these problems and is far from ready for the market.
What are product prototype assembly, adjustment, and finishing in manufacturing?
Unlike homemade prototypes, an engineered product prototype can have almost looked like the final product. Manufacturers ensure that the prototype has been assembled right; adjusted if need be and finished accordingly giving you a worthy sample to show off.
Whatever your requirements may be, do not hesitate to ask Sunrise Metal to produce an amazing prototype to wow your investors and clients.
What are product prototype testing and design evaluation in manufacturing?
The reason why people get prototypes is largely to test their designs. The aim is to have the product evolve during this stage rather than the manufacturing stage. Since all designs are different, your manufacturer may run prototype testing and design evaluation to see what unique challenges it presents.
Prototyping is a process of developing and adjusting until the design is ready for mass production.
What are the Best Practices for making A Product Prototype?
When you decide to make a product prototype, it doesn’t take one long to realize that having a plan will be beneficial in making the project a success. Here are top tips on the best practices for making a product prototype;
- Understand what you need – It can be very hard to explain what you require if you have a limited understanding of it yourself. Make sure you understand the defined goals of your product prototype to help your manufacturer create a prototype that works for you.
- Have specific goals for each prototype – You realize soon enough when you start prototyping that having a functional prototype is better than a pretty one. Work on proving your design concept rather than creating an aesthetically pleasing prototype.
- Learn what your provider can do for you to make the best out of your service. Ask questions to get a good understanding of your manufacturer’s capabilities. A good prototype provider will add value to the process by providing invaluable advice and experience.
- Know the limits of your prototype –Knowing what your prototype can and cannot do is great as you will know what iteration your product can and cannot do.
- Know the properties of your prototype material to make great products.
What are the differences between a homemade sample and an engineered product prototype?
Maybe you are wondering if you should make your own homemade sample or look for a manufacturer to do this for you.
Working with an expert gives you a good idea of what your prototype will look like when finished. It is made using the right materials and you can test for design, durability, and functionality, the engineered sample is closer to the final product than a homemade sample.
You can also expect that the quality will be higher than if you made it yourself or used 3D print. This will be beneficial if you want to market the product using the prototype. A well-manufactured prototype is good for investor meetings, exhibitions, and trade shows. It shows the people you are working with that you are serious about your idea as you have already invested cash to test it.
Will my prototype be as good as a finished product?
This is one of the questions that seems straightforward but isn’t. There are several stages in prototype development. The first prototype will be an idea of what you desire and cannot be the finished product.
Think of these prototypes as boasting fidelity, which is the degree to which they deviate from the actual thing. A lo-fi prototype will be nothing close to the final product as it only focuses on one aspect of the design. The good thing with prototypes is that they give designers the ability to test and improve on the design before it is a more complex design to change.
As the design continues to progress, the prototype will take the form of the final product. A beta version of the final product will definitely be closer to the real thing.
If you choose a reputable manufacturer, they are able to build a prototype and then text it. This evaluation helps show the weak areas needing changes and this can be amended before the second prototype. After repeating this process twice or thrice, the design is usually ready.
What is the typical timeframe for prototype development?
There is no answer to this that would suit all the types of prototypes. It really depends on the complexity of the design. If you have a simple design, it is easy to create and make improvements in a short time then scale to manufacturing.
A more complicated design with taking the design team a long time to develop a prototype, make edits and roll it out for manufacturing. Also, consider that your manufacturer may need additional time to optimize the design for you and maybe add some features like surface finishing. The timeframe, in short, is largely dependent on the design in question.
What should I consider before choosing a manufacturer for my product prototype?
From medical implants to larger structures for the great outdoors, prototypes are a versatile way to turn your design idea into reality. If you do decide to outsource, choosing the right partner is of paramount importance.
Firstly, consider that one manufacturer will handle the entire process so choose the one with the best capabilities. It sure helps that you can get an additional service if you need it.
Consider the capacity of the team you are working with. Can they handle your manufacturing needs? Will they provide the service in a good time?
It helps your team if your manufacturer has been in the industry for years. Not only does this give you peace of mind, but it also assures you of high-quality prototypes.
Sunrise Metal has dedicated its service to providing various manufacturing processes including prototyping. Do not hesitate to contact us should you have any questions regarding product prototyping. From conception and prototyping to finished production, Sunrise Metal offers an array of related services including die cast tooling and CNC machining.







