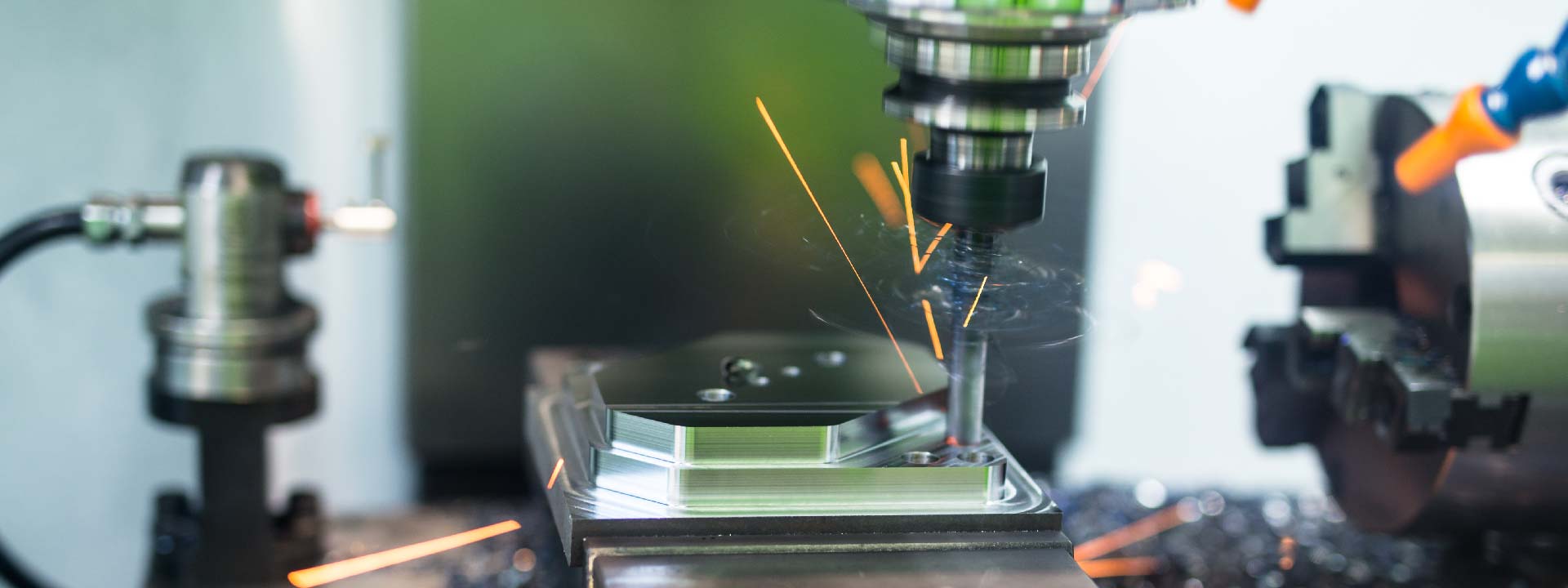
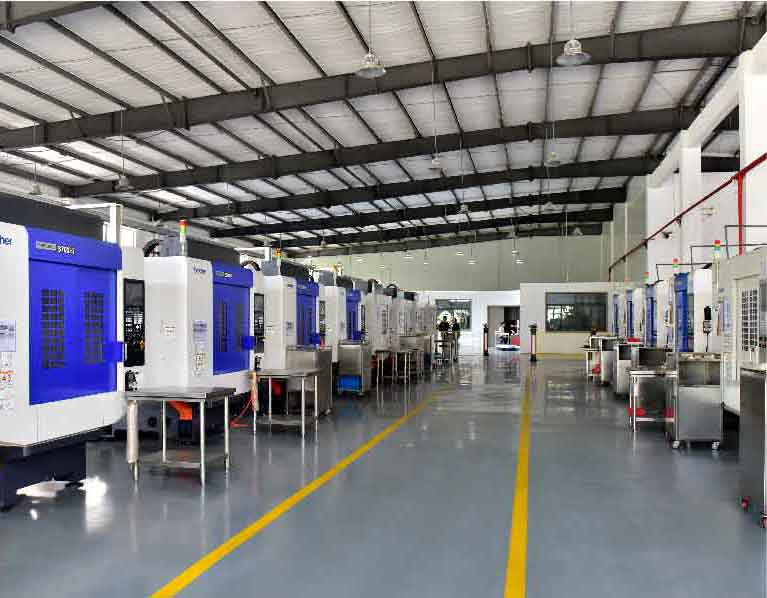
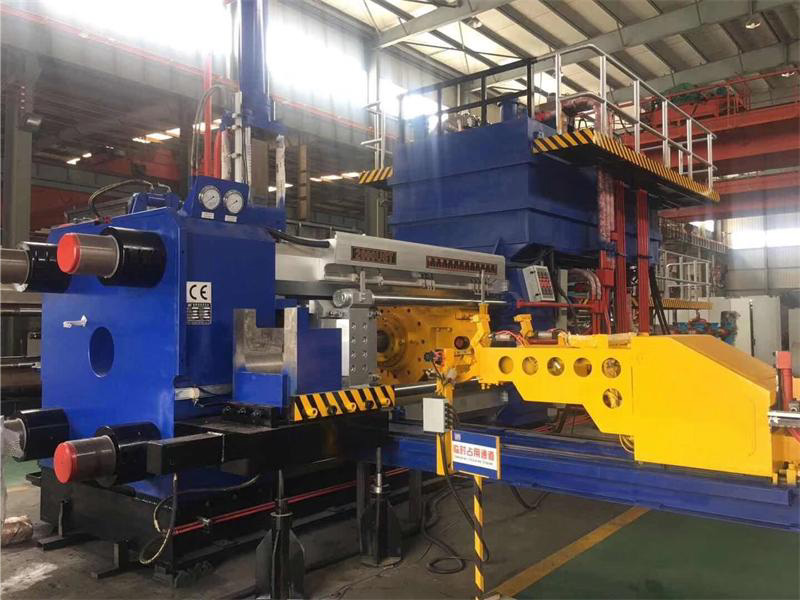
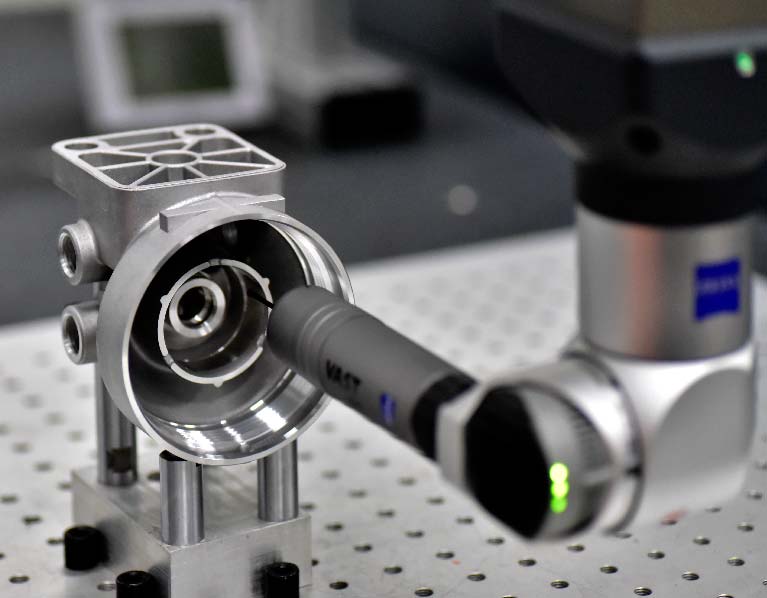
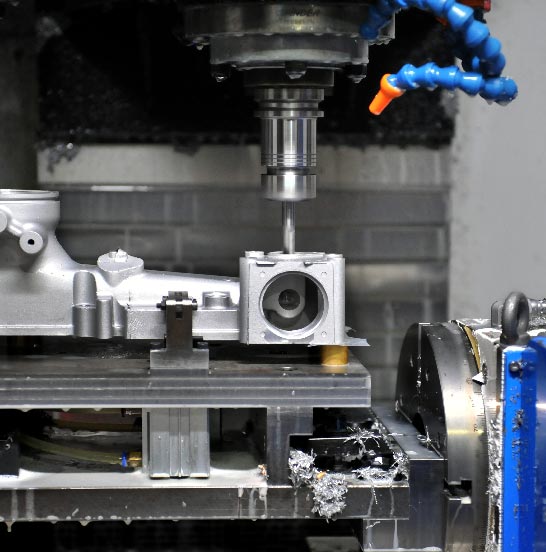
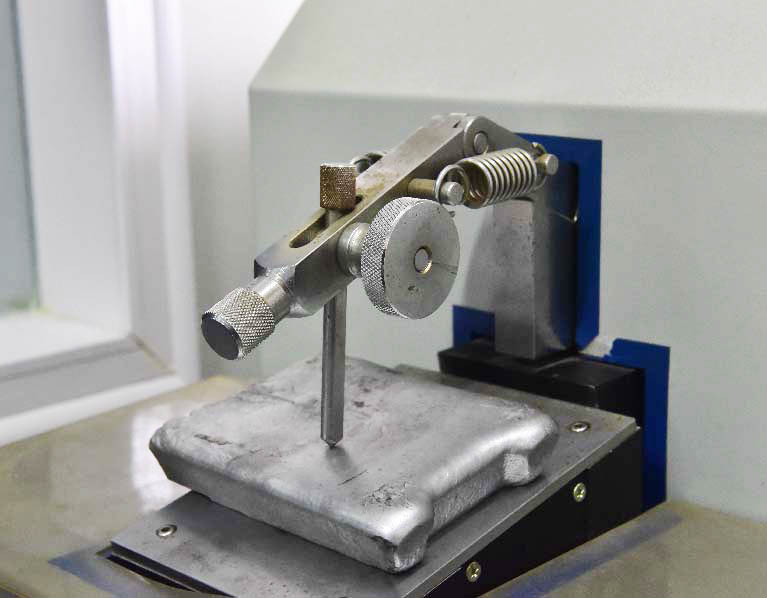
Your Prominent Extrusion machining Manufacturer in China
As a Key part of our 1-stop solution service, Sunrise Metal offers you the best of all Extrusion machining parts. Based on the quantity and complexity level, our outstandingly able engineers will give your best suggestion on how to make your part. For your long term but small-to-middle volume projects, you needn’t invest an expensive die casting mold, our Extrusion machining process is your best choice.
- Certified with ISO9001 and IATF16949, Sunrise Metal has both an effective quality control system, well-equipped latest inspection equipment. and a very Skillful QC team, which can assure 100% good quality of your Extrusion machining parts.
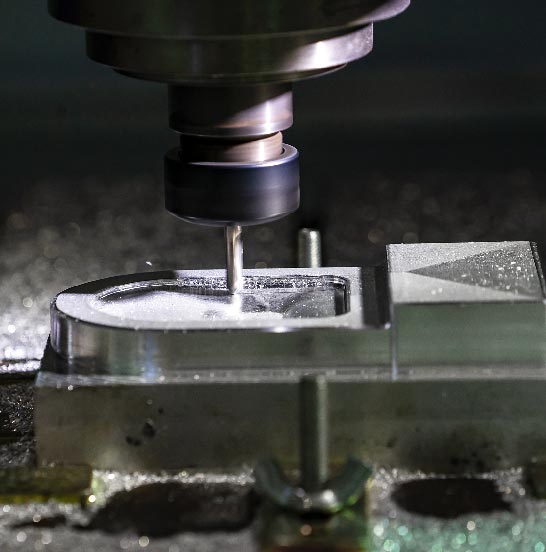
- Supported with our high advanced CNC machines— 2 sets 5 axes and 1 set 7 axes to include and our fast production system, we normally can save ½ lead time for your extrusion machining projects.
- We also provide matched surface treatment to your Extrusion machining parts, our know-how in surface treatment can bring your brilliant and memorable parts.
Sunrise Metal Makes Your Company Great with State-of-Art Extrusion machining Parts
Sunrise Metal Can Offer You More Value Added Service by Extrusion Machining Parts
Sunrise Metal has intensive experience with extrusion machining parts, we welcome your small quantity requests.
For your extrusion machining parts, we use Al6061 and Al6063 as main materials but if you have other needs, just specify it to us, we can follow your request.
We have one 6000T extrusion equipment, as our biggest extrusion line, the maximum section width it can extrude is about 580mm.
Consistent Investment & Upgrade Our Extursion Machining Manufacturing Equipment
Recent Extrusion Machining Projects
Sunrise Metal Has Served Many Global Customers with Extrusion Machining Parts.
- Stable And Creative Team
- Advanced Equipment
- Global Clients
- Premium Quality
- Fast Delivery
Our efficient and experienced engineering team is available to turn your design vision into a reality.

| No. | Name | Stroke | Q’ty |
| 1 | Mazak 7-axis turning&milling Machine | Ø658*1011MM | 1 |
| 2 | Mazak /Hass 5axis CNC machine | Ø850/Ø600 | 4 |
| 3 | 3-axis CNC machine center | 2000*1500MM | 1 |
| 4 | 4-axis CNC machine center | Ø250*800MM | 8 |
| 5 | 3-axis CNC machine center | 1000*600*600MM | 20 |
| 6 | CNC Lathes | Ø320*800/Ø610*1000MM | 2 |
| 7 | Sodick Wire cutting Machine | 400*400*200MM | 3 |
| 8 | EDM machine | 500*400*400MM | 2 |
| 9 | Surface grinder | 600*300*200MM | 1 |

| No. | Name | Brand | Q’ty |
| 1 | CMM | Carl Zessis | 1 |
| 2 | CMM | SanYou | 1 |
| 3 | Spectrometer | China | 1 |
| 4 | Microscope | China | 1 |
| 5 | Projector | China | 2 |
| 6 | X-ray Detector | SANDT | 1 |
| 7 | Cleanliness Test Equipment | China | 1 |
| 8 | Leakage Test Equipment | China | 2 |
| 9 | Salt Spray Testing Equipment | China | 1 |
| 10 | Pneumatic Measuring Instrument | China | 2 |
| 11 | Hardness Testing Machine | China | 1 |
| 12 | Color Meter Machine | China | 1 |
| 13 | Thickness Testing Machine | China | 1 |
| 14 | Electronic Balance | China | 1 |
| 15 | Density Balance | China | 1 |
Our commitment is to provide consistent, on-time delivery and enhance customers satisfaction at all stages.
Get A Free Consultation
Speak to an engineering consultant for your Rapid Prototyping parts to get customized suggestions and solutions based on your CAD and Step drawings.
Here is just a small part but an important way that we’re serving you on extrusion machining projects.
Sunrise Metal can offer full chain service if you have any needs for aluminum die casting. Looking learn more about aluminum die casting.
SUNRISE METAL EXTRUSION MACHINING:
THE COMPLETE FAQ GUIDE
Extrusion is known as a technique used to transform alloys (mostly aluminum alloys) into objects and parts with a precise and cross-sectional profile for a wide range of uses. The extrusion machining makes the majority of alloy’s exceptional combination of physical characteristics.
Alloys like aluminum have the malleability that licenses it to be expertly machined and cast, however then aluminum is 33% the density and firmness of steel, so the resulting parts offer strength and stability.
Today, extrusion machining is utilized for a more significant part of purposes, including segments of the International Space Station.
These various applications are possible profitable attributes of aluminum, from its particular blend of solidarity and flexibility to its conductivity, its non-magnetic properties, and its ability to be recycled on and on without loss of integrity.
These abilities make extrusion machining an available and versatile answer for a developing number of assembling needs.
- What is Extrusion Machining?
- What is the process of Extrusion Machining?
- What are the different types of Extrusion Machining?
- How the Aluminum Extrusion Machining Works?
- What shapes can be processed through Extrusion Machining?
- What is the after-processes of Extrusion Machining?
- What are surface finishes required and preferred after Extrusion Machining?
- Why Extrusion is a vital manufacturing process?
- What is the difference between Extruded Aluminum and Cast Aluminum?
- What are the advantages of Extrusion Machining?
- What is the Direct Extrusion Operation?
- What is the Indirect Extrusion Operation?
- On what temperature Aluminum Extrusion Machining operates?
- How helpful is the aluminum’s ability to conduct heat in Extrusion Machining?
What is Extrusion Machining?
Extrusion machining is a process by which alloy is constrained through a die with a particular cross-sectional profile.
A ground-breaking ram pushes the alloy through the die, and it rises out of the die opening. At the point when it does, it turns out in a similar shape as the die and is pulled out by emptying the die.
Machining plays an integral part in most extrusion works. Extrusion machining is possible to perform using a vast majority of machines including CNC machines, drills, tapping machines, presses, and punches. The selection of the most suitable machine for extrusion is determined by
- The production rate of parts
- Per batch parts quantity
- The actual fabrication specifications & details
- The parts quality requirements
- Tolerances of required parts
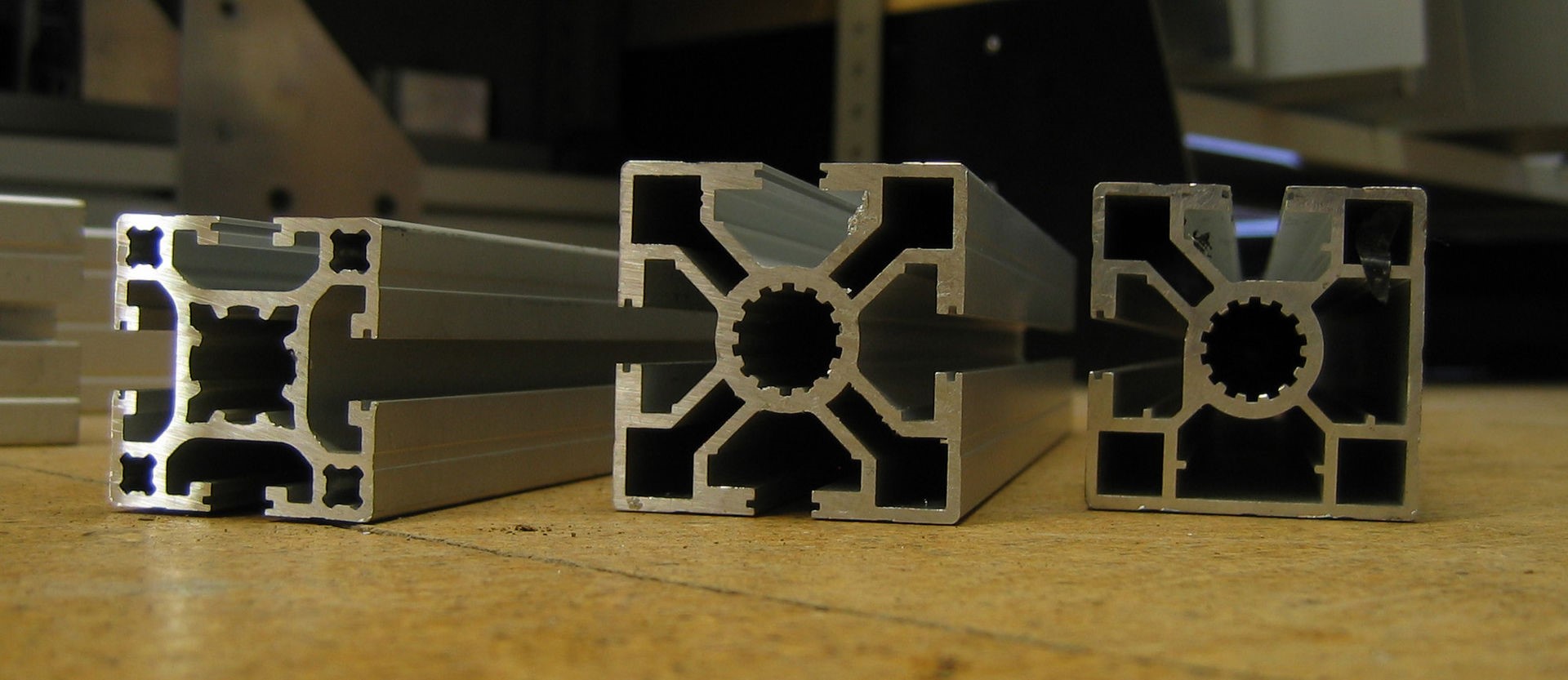
What is the process of Extrusion Machining?
The process of extrusion machining starts by heating up the stock material like aluminum (for hot or warm extrusion). Afterward, this metal is transferred into the press container.
A placement block is used behind it in the nearest location of the ram then pressed on the aluminum to empty the die by pushing it out. Then the extrusion is stretched to straighten the aluminum profile.
If better physical and mechanical properties are required, then it may be heat-treated or surface finish. The extrusion ratio is:
starting cross-sectional area / the cross-sectional area of the last extrusion
One of the core benefits of the extrusion machining is that this ration can be huge while still producing high-quality parts.

What are the different types of Extrusion Machining?
Extrusion machining is an assembling process that includes compelling base metal through a pre-molded die to shape objects and parts with exceptional shape and profile as the metal processed through the die, its shape changes by mirroring the die’s shape.
There are various sorts of extrusion machining, including cold, hot, friction, and micro.
- Cold Extrusion Machining: With cold extrusion, metal (for the most part aluminum) is constrained through the die while at or close to room temperature.
This metal comes in slugs, which are filled the die’s feeder, where pressure consolidates them to make a generous object/part in another shape.
- Hot Extrusion Machining: Hot extrusion includes heating metal at high temperatures and afterward driving it through the die while in a molten state.
We must utilize the correct temperature when performing hot extrusion. Furthermore, hot extrusion machining is an accurate and useful way to reshape metal.
- Friction Extrusion Machining: Friction extrusion machining includes the automatic rotation of the metal slugs/billets dependent on the die position. As the die pivots, it produces heat from the metal-on-metal friction around the section of the die.
This head permits the metal to go through the die all the more rapidly. Friction extrusion machining is effective and efficient that’s gaining popularity among manufacturers.
- Micro Extrusion Machining: Micro extrusion is characterized by the ability to manufacture small, micro-sized parts. Notably, the cross-section of the die supports base metal estimating only 1 millimeter.
Its profoundly technical nature of making little objects that can withstand excessive pressure, it has increased a significant level of popularity.
How the Aluminum Extrusion Machining Works?
Aluminum extrusion is a machining process by which aluminum is processed through the die with a particular cross-sectional profile and yield a wholly created and molded aluminum part.
Aluminum extrusion has unlimited applications over a wide scope of industries, including architectural, automotive, electronics, aviation, power & energy, and other potential industries.
Furthermore, the structural complex-shaped parts can be manufactured easily through aluminum extrusion machining.
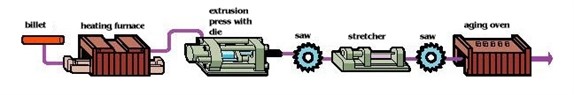
The working of aluminum extrusion machining is clarified through a ten-step guide.
- The extrusion machining dies preparing and locating to the extrusion press is the most initial step.
- Before extrusion, the aluminum billet, which is going to be processed, is preheated.
- Afterward, the aluminum billet is carried out to the extrusion press.
- A ram pushes the billet (aluminum billet) all the way into the container.
- The extruded and processed aluminum rises through the die.
- The extrusion is tracked along with the runout table and quenched.
- Later, these extrusions are accurately sheared to the length-table.
- It’s essential to cool the extrusions to the room temperatures.
- Afterward, the extrusions are moved to a stretcher which extruded the aluminum into arrangements.
- The final step is to transfer the extrusions to the finish saw and cut them according to length requirements.

What shapes can be processed through Extrusion Machining?
The extruded shapes are divided into three main categories:
- Solid: With zero encased voids and openings like pole, beam, or point.
- Hollow: With one or more voids like a square or rectangular tube.
- Semi-Hollow: With a partially enclosed void like ‘C’ channel with a narrow gap.
(Aluminum Angle & Drawing)

(Aluminum Channel & Drawing)

(Round Tube & Drawing)

What is the after-processes of Extrusion Machining?
When the extrusion is finished, profiles can be heat treated to upgrade their properties, and other surface finishes additionally can be applied to improve their appearance and corrosion-resistance.
These surface finishes can be anodization, painting, powder coating, sandblasting, or sublimation ultimately depends on the final product requirement and properties.
The parts additionally can be prepared through fabrication tasks to carry them to their last measurements. Clients need to comprehend the quality needs of their undertaking to guarantee the correct decision of alloy and temperature.
What are surface finishes required and preferred after Extrusion Machining?
Aluminum profiles can undergo a vast majority of finishing operations. The two primary reasons to consider these are that they can upgrade the presence of the aluminum parts and can likewise improve its corrosion-resistance and physical properties, and there are different benefits also.
For example, the anodization process thickens the aluminum’s naturally-occurring oxide layer, improving its corrosion-resistance.
Likewise, making the aluminum increasingly resistant to wear, improving surface emissivity, and giving a porous surface that can acknowledge diverse colors.
Other finishing processes, for example, painting, powder coating, sandblasting, and sublimation (to make a wood-look), can be experienced too.

Why Extrusion is a vital manufacturing process?

The procedure of aluminum extrusion machining is for assembling exceptional cross-sectional profiles. The process starts by pushing the heated aluminum through a die. The shapes produced through extrusion machining can be reliable, hollow, or semi-hollow and these shapes can be basic or muddled.
This is an entrancing and supreme procedure and also can manage 24-foot complex profiles. Afterward, these profiles are able to heat-treated, finished, and fabricated according to the customers’ requirements & specifications.
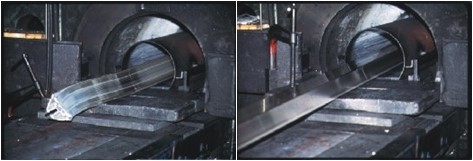
These figures show a new length of extrudate just emerging from the press (left) and the production of a profile in progress (right).
What is the difference between Extruded Aluminum and Cast Aluminum?
Aluminum is exceptionally versatile and is an excellent option for a vast majority of manufacturing methods, two of which are extrusion and casting.
The difference between them is one of the most asked questions. Extrusion is a process by which alloys are constrained through a die, bringing about the ideal cross-section.
However, casting is a process in which molten aluminum is poured into a mold and then allowed to solidify. Each method of manufacturing aluminum parts has unique advantages.
Whether you think you require aluminum extrusions or are considering aluminum casting, you can always count on Sunrise Metal to point you in the right direction.
(Extruded Aluminum Architectural Shapes)


What are the advantages of Extrusion Machining?
Extrusion Machining is a better option in many ways. Some of its essential advantages are the following:
- Low industrial cost
- More economical in high-production of parts that require excellent dimensional accuracy
- Better surface finish
- A better option in shorter production runs due to lesser start-up costs
- The flexibility of operation
- Proper mixing (compounding)
- Continuous operation
- Excellent mechanical properties obtained in extrusion machining
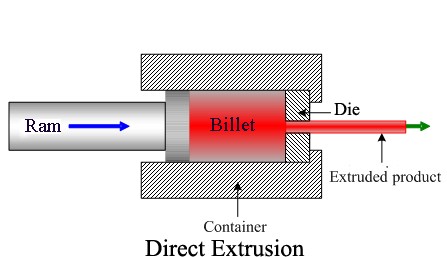
What is the Direct Extrusion Operation?
After the required shape for a finalized part has been finalized and an appropriate aluminum alloy is selected, an extrusion die, and associated tooling is produced.
In the actual extrusion process, the aluminum alloy and extrusion tools are preheated. During the extrusion, the alloy is still solid but has been softened in a furnace.
The extrusion process officially starts when the press ram is ready and begins to pressurize the alloy inside a container. Hydraulic presses can apply from 100 tons to 15,000 tons of pressure; the pressure limit of a particular press decides how enormous an extrusion it can create.
As pressure is applied, the alloy is first squashed against the die, getting shorter and more extensive until the container dividers confine its development.
A short time later, as the pressure expands, the delicate aluminum has no spot else to go and starts to crush out through the molded die to develop on the opposite side as a full-fledged profile.
The formed part is cut off at the die, and the rest of the aluminum is expelled to be recycled completely. After the die is empty, the still-hot extrusion might be extinguished, mechanically treated, to impart wanted metallurgical properties and physical execution.
After sufficient aging, regardless of whether in an aging oven or at room temperature, the profiles are moved to different territories of the plant and might be done (painted or anodized), fabricated (cut, machined, bowed, welded, assembled), or pressed for shipment.
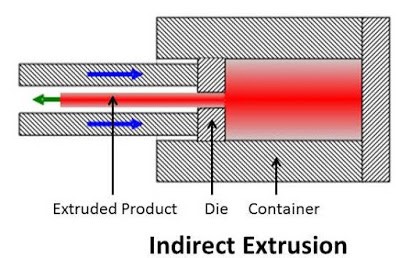
What is the Indirect Extrusion Operation?
This is an entirely unique method; the die stays in its permanent place while the aluminum billet plus the container move. This movement is unison, and the pressure of the ram forces the metal, which is transformed into a soft material to flow through the die opening in the opposite direction of the ram.
This is also called backward extrusion because the process remains the same but in the opposite direction.
The extrusion could be a continuous process, to output significant components, or semi-continuous, to produce parts rapidly, and the size of the parts can be from one millimeter to many feet.
Extrusions through machining can be fabricated in different complex shapes because of the aluminum’s malleability and weight, such as hollow and multi-chamber profiles that are nearly impossible to achieve with any other metals.
At what temperature, Aluminum Extrusion Machining operates?
During extrusion machining, balancing and maintaining the temperature and controlling it is a crucial step of the complete process. The container temperature must remain constant in every situation during the cycle, front to back & top to bottom.
The temperature of the aluminum alloy, which is being used, is limited by the shape being extruded. Additionally, lower extrusion temperatures usually produce shapes with exceptional quality surfaces and accurate dimensions, while excessive temperatures may decrease the tensile strength.
The aluminum’s melting point is approximately 1,210° F (654° C).
Extrusion machining operations take place with billet heated to the temperatures above 705°F (374°C), and – mostly depends upon the aluminum alloy being processed & extruded – as high as 940°F (504°C).
How helpful is the aluminum’s ability to conduct heat in Extrusion Machining?
The aluminum’s ability to conduct heat makes it an ideal metal for industrial use as heat shielding or heat transfer components.
The extruded aluminum parts surface can be finished in the vast majority of ways, such as anodizing, painting, and powder-coating.
Each finish creates a coating with exceptionally unique characteristics that can be used in commercial, industrial, and consumer applications.