HOT CHAMBER VS COLD CHAMBER DIE CASTING
Cold Chamber Die Casting and Hot Chamber Die Casting are variations of the High-Pressure Die Casting process. So, the process of both hot and cold chamber casting is quite similar. However, their scope of application is different from one another. This article will briefly discuss the differences between these two processes in detail.
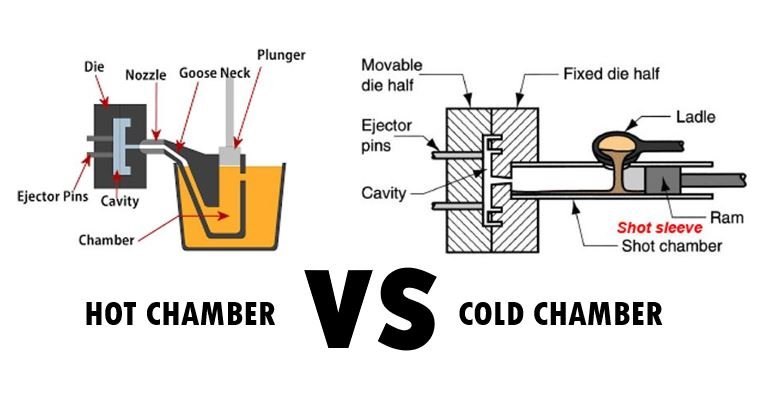
Temperature Range
Hot chamber equipment deals with non-ferrous alloys of low temperature. The maximum temperature of alloys that can be safely die cast in a hot chamber machine is around 450°C, which includes alloys of Zinc, Magnesium, Lead, etc.
On the contrary, cold chamber equipment deals with non-ferrous alloys of high temperature. It usually handles metal alloys with a temperature at or above 600°C, including alloys of Aluminum, Copper, Brass, etc.
Furnace Location
The alloy melting furnace is located in different places for both processes. Hot chamber equipment has a built-in furnace to melt the metal. So, the metal is directly sent to the die cavity through a gooseneck.
In a cold chamber die casting setup, the melting furnace is located outside. The molten metal has to be carried into the machine using an automated or manually operated ladle.
Production Time
Hot chamber machines offer noticeably higher casting cycles than cold chamber machines. Despite both of the equipment work quite similarly, cold chamber casting has a longer cycle due to manual handling of molten metal.
Tool Life
Hot chamber and cold chamber machines are constructed using the same materials. Hot chamber casting utilizes low melting point alloys, which have less impact on the die. So, it lasts longer. On the contrary, the die condition for cold chamber machines degrades faster as the melted metal has a higher temperature.
| HOT CHAMBER DIE CASTING | COLD CHAMBER DIE CASTING |
| Die casting alloy is melted in a furnace located within the equipment | Die casting alloy is melted in a separate furnace located outside the equipment |
| Casting cycles are significantly shorter, thus has a higher production capacity | Has longer casting cycles; thus, the production capacity is less |
| Suitable for low melting point alloys | Suitable for high melting point alloys |
| Offers longer tool life | Has shorter tool life |
| Requires minimum safety measures | Requires more safety measures |
| Commonly used metal alloys include Zinc, lead and etc. | Commonly used metal alloys include Aluminum, Copper, Brass,Magnesium, etc. |
Sunrise Metal Offers Exclusive Hot and Cold Chamber Die Casting Service
Sunrise Metal is a die casting manufacturing company in China with strong core competencies. We have multiple factories equipped with advanced hot chamber and cold chamber equipment. Below we have provided an overview of our Hot Chamber Die Casting Services and Cold Chamber Die Casting Services.
Cold Chamber Die Casting Service

Our strong side is our cold chamber casting capabilities, and we are an expert in aluminum die casting. Right now, we have ten cold chambers die casting equipment for aluminum die casting. Our material choice for cold chamber casting includes,
- ADC12
- A380
- AlSi9Cu
- AlSi10, and many more.
All of the machines are from renowned manufacturers like LK Machinery, Buhler, Toshiba, Yizumi, etc. Moreover, we have machines of diverse specifications. The equipment capacity ranges from 280T to 1600T. Therefore, we are capable of handling any small to large volume die casting projects.
Furthermore, we have in-house cleaning and surface finishing facility for the die cast parts. So, you can get a one-stop cold chamber die casting solution from us.
Hot Chamber Die Casting Service

Our hot chamber die casting equipment are of varying tonnage capacities ranging from 60T to 250T. So, we can handle a diverse range of die casting projects. We mainly use the hot chamber equipment for zinc die casting.
We mainly use the Zamak 3 and Zamak 5 alloy for hot chamber production. And, we are an expert in zinc polish and chrome plating.
Hot or Cold Chamber Casting, Which One is Better?
Hot and Cold Chamber Die Casting are both excellent for producing metal parts. But, the hot chamber process has some advantages over the cold chamber process. It is faster, economical, less hazardous, and provides longer tool life than the cold chamber process.
These properties can easily convince one to believe that hot chamber casting is better than cold chamber casting. However, their scope of application is different. So, it is hard to rule out one method to be better than the other based on their relative advantages.
Hot and cold chamber casting deals with entirely different varieties of alloys. For example, you can only die cast aluminum in a cold chamber environment. Simply put, you don’t have much of an option when you are dealing with high melting point alloys like aluminum.
So, you have to focus on which alloy to use rather than which process. You have to choose the right alloy that will meet the requirements of your parts. Your choice of alloy will decide the necessary means of production.
How to Deal with the Disadvantages of the Cold Chamber Process?
The melting furnace and main die casting equipment are separate in a cold chamber setup. So, the molten die casting alloys to be transferred to the shot cylinder via a ladle. Most manufacturers deploy a worker to pour the molten metal manually.
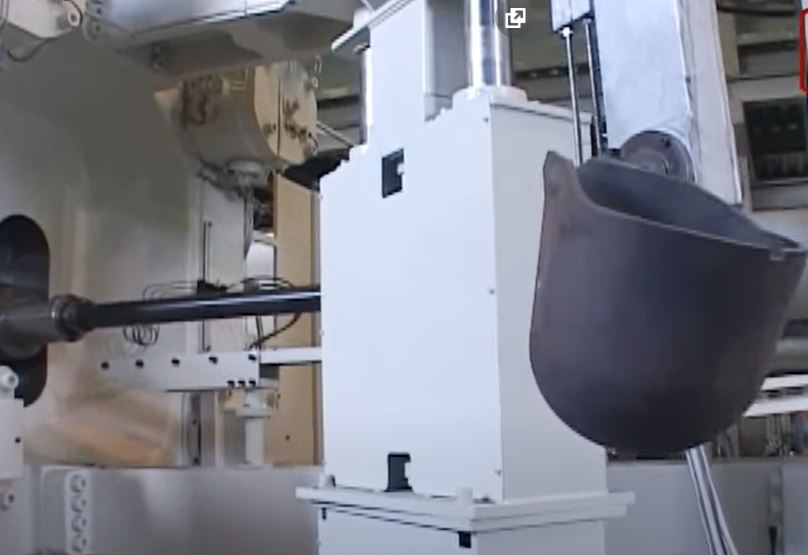

The molten metal is handled in the open air in a cold chamber process. There are potential risks for accidents and blowback during the injection of metals. So, the manufacturers should take proper measures to ensure the safety of the workers. The worker should have the safety gears on and always close the door of the equipment before injection.
However, this step can be replaced by a robot arm to automate the process. It would both increase production efficiency and eliminate the potential hazards involved in the process. It would also reduce the labor cost as well.
Is Hot Chamber or Cold Chamber Process Good for Automotive Applications?
The automotive industry is a big sector. Automobile manufacturers utilize a wide range of processes and materials for building up a vehicle from scratch. Although, the majority of automotive parts are made up of aluminum alloys.
It is because automotive applications require lightweight parts to reduce fuel consumption. Moreover, the parts must have sufficient mechanical strength, high corrosion resistance, and should be able to withstand high temperatures.
In that sense, any process best suited for manufacturing aluminum parts can be considered ideal for the automotive industry. Since aluminum requires cold chamber die casting, it can be considered better for automotive applications.
Note that hot chamber die casting also has a fair amount of application in the automotive sector. It is used to cast some magnesium and zinc alloy parts. But the production volume is comparatively lower.





