Die Casting Alloys
Die casting alloys are marked with their superior properties and excellent surface finishes. The metals that can be die casted are namely zinc, aluminum, and magnesium.
Sunrise die casting alloys mainly focus on aluminum alloys such as ADC12, A380, AlSi12, etc. However, depending on the type of application, we choose the best material to fit projects.
Each die cast alloy offers a unique benefit but aluminIum stands out as the die casting alloy to withstand the highest operating temperature and conditions. Its alloys are lightweight but also as strong as construction steel, and highly elastic for use under shock loads.
Advanced and technologically-tested production methods facilitate the creation of die casting options suitable for an extensive range of industries. Looking to know more about aluminum die casting.
Sunrise Aluminum Die Casting Manufacturing Capability
Benefit from the many possibilities offered by our aluminum die cast alloy production processes while maintaining the highest standards in the industry. Sunrise Metal, as an expert aluminum die casting factory, stands out in the field and is ready to help you meet challenging industrial needs!



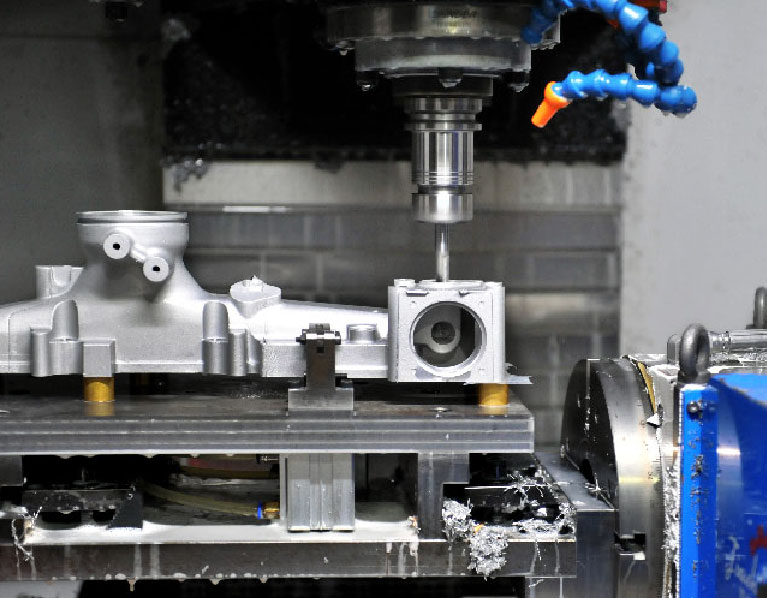


Advanced Equipment For Die Casting Manufacturing
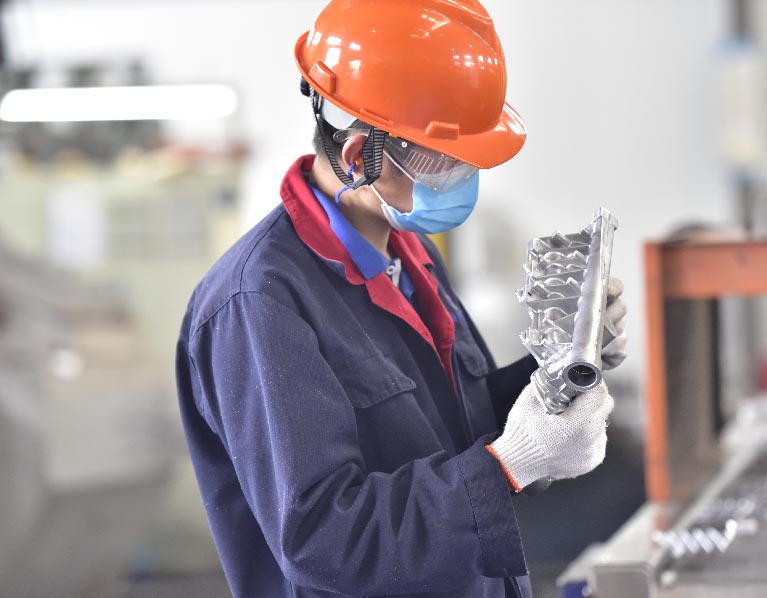
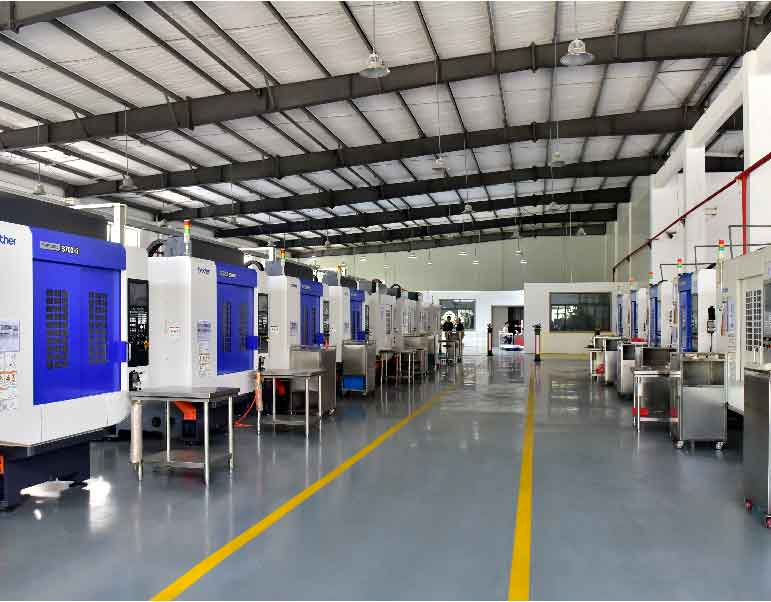






General Aluminum Material

ADC12 is equivalent to A383, if your part is highly complex, ADC12——is often used as an alternative to ADC10. And it is applied to Cold Chamber Die Casting process.
It has better corrosion resistances, is lightweight, and its benefits include ease of casting, good mechanical properties, and dimensional stability.
MECHINICAL PROPERTIES
Elongation: 3.5% in 50mm
Tensile strength: 310 MPa
Yield Strength(0.2%): 150MPa
Impact Strength: 4 J
Hardness: 75 HB
PHYSICAL PROPERITIES
Density: 2.74g/cm³
Melting Point: 549℃
Thermal Conductivity: 96 W/mk
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: 21.1 μm/m°k
Electrical Conductivity: 23.0 % IACS

A380 is equivalent to ADC10, which is one of the most commonly specified aluminum alloys in Cold Chamber Die Casting with a number of significant benefits:
- Best combination of casting, mechanical, and thermal properties
- Excellent fluidity, pressure tightness, and resistance to hot cracking
- Wide variety of products including chassis for electronic equipment, engine brackets, gearbox cases, household furniture, power, and hand tools
MECHINICAL PROPERTIES
Elongation: 3.5% in 50mm
Tensile strength: 324 MPa
Yield Strength(0.2%): 160MPa
Impact Strength: 4 J
Shear Strength: 190MPa
Hardness: 80 HB
PHYSICAL PROPERITIES
Density: 2.71g/cm³
Melting Point: 566℃
Thermal Conductivity: 96 W/mk
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: 21.8 μm/m°k
Electrical Conductivity: 23.0 % IACS

is one of the most commonly specified aluminum alloys in Cold Chamber Die Casting with a number of significant benefits:
MECHINICAL PROPERTIES
Elongation: 3.5% in 50mm
Tensile strength: 324 MPa
Yield Strength(0.2%): 160MPa
Impact Strength: 4 J
Shear Strength: 190MPa
Hardness: 80 HB
PHYSICAL PROPERITIES
Density: 2.71g/cm³
Melting Point: 566℃
Thermal Conductivity: 96 W/mk
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: 21.8 μm/m°k
Electrical Conductivity: 23.0 % IACS

Zamak 5 or Zinc Alloy 5#, is the most widely used zinc alloy in Europe. And it is applied to Hot Chamber Die Casting.
- higher copper content than Zamak 3, which results in higher strength
- less ductility (decreased elongation) than Zamak 3
- Reduction in ductility can affect formability during secondary operations such as bending, riveting, swaging, or crimping operations
- If need a measure of tensile performance, Zamak 5 castings are recommended.
- Zamak 5 is more readily plated, finished, and machined than Alloy 3
MECHINICAL PROPERTIES
Elongation: 7% in 50mm
Tensile strength: 328 MPa
Yield Strength(0.2%): 228MPa
Impact Strength: 65 J
Shear Strength: 262MPa
Hardness: 91 HB
PHYSICAL PROPERITIES
Density: 6.60g/cm³
Melting Point: 388℃
Thermal Conductivity: 109W/mk
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: 27.4 μm/m°k
Electrical Conductivity: 26.0 % IACS

Zamak 3 or Zinc Alloy 3#, is the most widely used zinc alloy in North America and is usually the first choice when considering zinc for die casting for a number of reasons.
And it is applied to Hot Chamber Die Casting.
- Excellent balance of desirable physical and mechanical properties
- Superb castability and long-term dimensional stability
- Excellent finishing characteristics for plating, painting, and chromate treatments
- Excellent damping capacity and vibration attenuation in comparison to aluminum die cast alloys
When it comes to die casting, Zamak 3 is the standard by which other zinc alloys are rated.
MECHINICAL PROPERTIES
Elongation: 10% in 50mm
Tensile strength: 283 MPa
Yield Strength(0.2%): 221MPa
Impact Strength: 58 J
Shear Strength: 214MPa
Hardness: 82 HB
PHYSICAL PROPERITIES
Density: 6.60 g/cm³
Melting Point: 384℃
Thermal Conductivity: 113 W/mk
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: 27.4 μm/m°k
Electrical Conductivity: 27.0 % IACS

- Corrosion resistance is achieved by enforcing very strict limits on three metallic impurities—iron, copper and nickel. These are limited to very low levels making it necessary to use primary magnesium in the production of this alloy
- As with all magnesium alloys, special precautions must be taken when machining
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES
Elongation: 3% in 50mm
Tensile strength: 230 MPa
Yield Strength(0.2%): 160MPa
Impact Strength: 3 J
Shear Strength: 140MPa
Hardness: 63 HB
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
Density: 1.81g/cm³
Melting Point: 533℃
Thermal Conductivity: 72 W/mk
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: 25.2 μm/m°k
Electrical Conductivity: 12.2.0 % IACS
DIE CASTING ALLOYS: THE ULTIMATE FAQ GUIDE
In general, die casting alloys are considered as non-ferrous.
However, their large number accessible with a variety of physical and mechanical properties, enabling itself in almost every conceivable application.
Aluminum alloys are the most common and widely used and sometimes are followed by silicon and copper.
Lightweight alloys offer a perfect amount of corrosion resistance, casting ease, and possess excellent mechanical and physical properties, as well as dimensional stability, are preferred for die casting.
Die casting process is outstanding for its ability to deliver/produce leaves behind a high level of consistency, plan exactness, and excellent surface finishes.
The determination of the best alloy for die casting can dispose of the requirement for after creation machining, raising the creation and process cost-productivity and shortening manufacturing time.
- What are the characteristics of Aluminum Die Casting alloys?
- What are the advantages of Aluminum in Die Casting?
- What are the main reasons for using aluminum in Die Casting?
- What are the Most effective alloys for Die Casting?
- Which mechanical properties are preferred in Die Casting for the selection of suitable alloys?
- Which physical properties are preferred in Die Casting for the selection of suitable alloys?
- What role alloy cost plays while selecting the optimum Die Casting alloys?
- How to define the process cost of Die Casting alloys?
- What are the structural properties of Die Casting alloys?
- What is the lightweight alloy of the Die Casting?
- What is the role of impact strength and dent resistance of Die Casting alloys?
- What is the importance of corrosion resistance for Die Casting alloys?
- What is the bearing properties and wear resistance of Die Casting alloys?
- What is the machinability of Die Casting alloys?
- How does the heat treatment work for aluminum Die Casting alloys?
- What are the characteristics of Aluminum Die Casting alloys?
- What is the Silicon in Aluminum Die Casting alloys?
- What is the Copper in Aluminum Die Casting alloys?
- What are the famous fields of applications of Aluminum Die Casting alloys?
- What is the history of Die Casting alloys?
- What to consider when selecting a Die Casting Material?
- What are the casting characteristics of die casting alloys?
What are the characteristics of Aluminum Die Casting alloys?
Aluminum helps when selected as a Die Casting alloy and enables us to take advantage of its different characteristics which are the following:
- Can operate in high temperatures
- Exceptional corrosion resistance
- Lightweight
- Holds a high level of strength and hardness
- Fine strength-to-weight ratio
- Offers EMI/RFI shielding properties
- Offers good finishing characteristics
- High-level of electrical conductivity
- Fully recyclable
- Environmentally friendly
What are the advantages of Aluminum in Die Casting?
One of the most preferred advantages of using aluminum alloys in die casting is that it helps to produce lightweight parts with a vast majority of surface finishing options.
Aluminum can withstand the most elevated temperatures and highly corrosion-resistance.
Furthermore, aluminum retains high-level of dimensional stability with thin walls and can be used anywhere (almost in every industry).
What are the main reasons for using aluminum alloy in Die Casting?
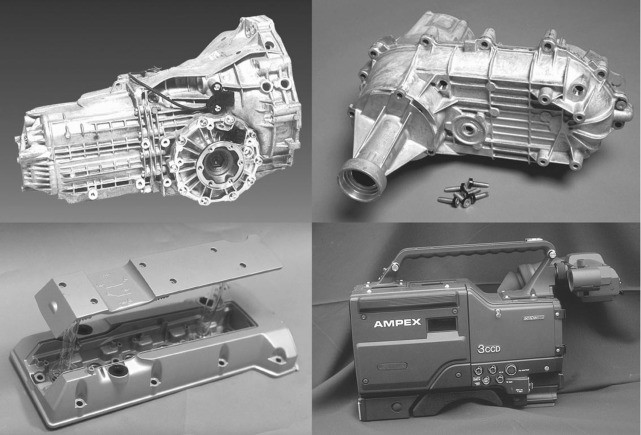
The following are some of the most unique and main reasons for using aluminum alloys in die casting:
- Helps to improve the automation fuel efficiency by decreasing the weight of components.
- Have more noteworthy use in systems administration and framework gear in the telecom and figuring enterprises.
- Give EMI/RFI shielding, execution, and sturdiness on account of its lightweight property.
- It’s extraordinary electrical-execution in addition to shielding properties, even in high working temperatures situations, aluminum alloys demonstrated perfect for gadgets, lodging, and clinical hardware.
What are the Most effective alloys for Die Casting?
There are four most effective alloys used in die casting in-order-to manufacture/produce top-quality products.
Aluminum Alloy A380: It’s the most common and most preferred only specified for die casting with many significant advantages.
Aluminum Alloy ADC12 (383): Highly indicate die casting alloy and holds excellent mechanical properties.

Aluminum-Silicon Alloy AlSi12: Die casting alloy with high hardness, and exceptional wear resistance also offers excellent pressure tightness.

Aluminum-Silicon-Copper Alloy AlSi9Cu: Offers exceptionally perfect pressure tightness and fluidity.
Which mechanical properties are preferred in Die Casting for the selection of suitable alloys?
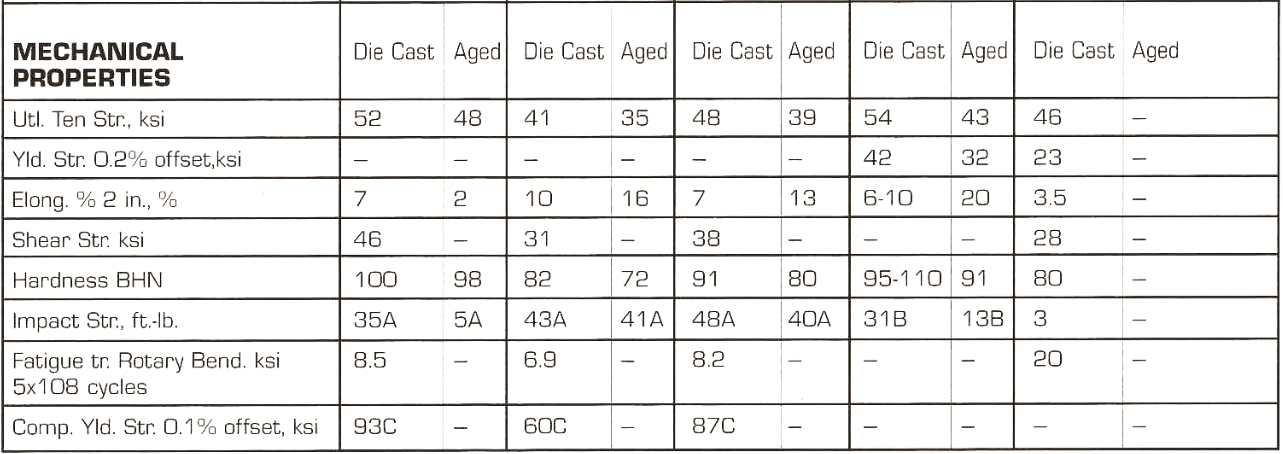
Mechanical properties that are considered as essential and the qualified alloys must possess them are the following described.
- Elongation: Unit (% in 50mm)
- Tensile Strength: Unit (MPa)
- Yield Strength (0.2%): Unit (MPa)
- Impact Strength: Unit (J)
- Shear Strength: Unit (MPa)
- Hardness: Unit (HB)
Which physical properties are preferred in Die Casting for the selection of suitable alloys?
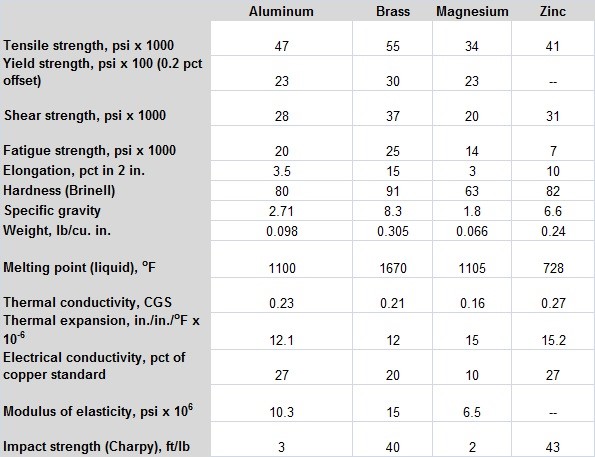
Physical properties that are considered as essential and the qualified alloys must possess them are following described.
- Density: Unit (g/cm3)
- Melting Point (Average +/- 50): Unit (°C)
- Thermal Conductivity: Unit (W / m K)
- Coefficient of Thermal Expansion: Unit (µm/m°K)
- Electrical Conductivity: Unit (% IACS)
What role alloy cost plays while selecting the optimum Die Casting alloys?
Die casting alloy cost proven an essential factor in overall product cost.
Nonetheless, alloy cost will, in general, vary with economic situations, so any thought and remarks must be general.
The alloys cost is depended on weight; however, on the other hand, the design is based on the volume of material.
The volume of die-casting alloy can be optimized for aluminum, silicon, and copper, generally, be neatly constant.
In this manner, cost-per-cubic-inch is a perfect estimate of relative die-casting material cost.
Aluminum die-casting alloys usually have the lowest cost-per-cubic-inch and accounts for its ordinary use.
How to define the process cost of Die Casting alloys?
Consideration of process cost is essential in overall production and product cost.
There are four crucial factors to consider when it comes to process cost, which is the following:
- Die casting alloys that are appropriate for hot-chamber cast ordinarily require littler die casting machines that run at a quick pace of creation when contrasted with size casting that sudden spikes in demand for cold-chamber machines.
- The unrerlying costs (counting producing costs) is likewise a fundamental part to consider, paying little mind to the die casting composite.
By and large, die upkeep and substitution costs are likewise changed. These expenses are lower for zinc alloys because Zinc doesn’t assault/harm die steels and can be cast at low temperatures.
These costs increase with aluminum alloys because of its hardness and temperature properties.
- Most die casting alloys may diminish/dispose of the surface, completing tasks when accuracy highlights are necessarily required.
For example, zero draft and press-fit tolerances, which can regularly be thrown in magnesium, Zinc, and ZA alloys.
- The majority of Zinc and few of aluminum alloys tend to be the materials of choice for ultra-small die casting (normally > 28g).
This advantage is credited to enterprises that have created one of a kind reasons, exceptionally robotized machines that produce die casting at pitiful procedure costs.
What are the structural properties of Die Casting alloys?
Mechanical and physical properties of die casting alloys to display the mid-run modulus of the versatility of the four alloy gatherings.
Furthermore, their relatively high strength – low density makes them the numerous selection choice for medium to large die casting with essential structural requirements.
Magnesium alloys, with lower quality and rigidity, are dangerous with Aluminum alloys in specific applications/models by creating frameworks meager, deliberately found strengthening ribs.
In applications that require most exceptional quality inside a predefined space, Zinc and Aluminum alloys offer the most noteworthy extreme and yield qualities moreover, modulus of versatility, and are the best decision.
However, aluminum die-casting alloys to maintain their structural properties over a more comprehensive operating temperature range as compared to the other alloy groups.
Their security once in a while makes them the die casting alloys of the decision at raised working temperatures, for the most part where least/no measure of creep is admissible.
Then again, the downer attributes of Zinc and ZA alloys are like the thick flexible conduct of thermoplastics and need to consider when long haul supported burdens initiate moderate to high-feelings of anxiety.
Research papers and information are accessible that empower the creator to foresee combination conduct and adjust the plan when required.
What is the lightweight alloy of the Die Casting?
When it comes to a lightweight die casting alloy, aluminum alloys are a perfect choice.
Furthermore, the environment or equipment where the weight requirements is a significant decision.
However, other criteria such as mechanical/physical properties or cost are also critical to consider, and aluminum alloys are one again is the best option.
What is the role of impact strength and dent resistance of Die Casting alloys?
The aluminum and zinc alloys offer a high-level impact strength as compared to the other die casting alloys.
Be that as it may, the effect quality of zinc alloys starts to decrease pointedly as working or natural temperature is diminished beneath 32-degree F (0 degrees C).
And that leaves us only with the Aluminum die casting alloys.
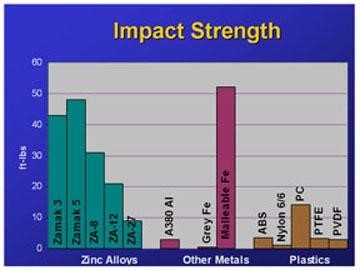
Dent resistance, as can be seen, is demonstrated by the ratio of yield strength to modulus versatility.
Somehow, for identical features with equal wall thickness, most of the aluminum alloys offer an exceptional amount of dent resistance.
The zinc alloys have a lower yield strength; however, their non-linear modulus of elasticity enables then to extend the storage capacity of elastic energy as compared to the yield strength to modulus of elasticity ratio includes.
Furthermore, it increases the level of its dent-resistance.
Zinc alloys may be considered slightly below from the majority of aluminum alloys, and mostly superior magnesium alloys.
The yield strength to modulus of elasticity rations of aluminum alloys is nearly equal to the zinc alloys mentioned.
What is the importance of corrosion resistance for Die Casting alloys?
The pragmatic contrasts and changes in corrosion resistance can happen inside the die casting alloys, especially aluminum and magnesium alloys.
Aluminum alloys fluctuate as indicated by concoction creation, especially copper substance, and magnesium alloys differ with metal immaculateness.
The remaining alloys offer moderate corrosion resistance.
However, the corrosion resistance of aluminum die casting alloys can be enhanced and improved further, as required, with a variety of low-cost surface-finishing/surface-treatment systems.
What is the bearing properties and wear resistance of Die Casting alloys?
All die casting alloys can be used for hydrodynamic bearing applications; however, our industry prefers aluminum alloys.
Furthermore, this enhancement took place where oil is fed to the bearing under pressure, and a dull oil film is required to maintain by rotation of the journal in bearing.
Where the only option is partial lubrication, the aluminum alloys offer a minimal amount of resistance to abrasion and wear.
What is the machinability of Die Casting alloys?
The most energizing thing about die casting alloys is that they offer excellent to uncommonly brilliant machining qualities while machining activities are required.
Aluminum alloys show moderate variety.
Aluminum and magnesium both offer the ideal machinability of any auxiliary metal concerning instrument life, least measure of vitality utilization, and low cutting powers prerequisites.
In any case, for some particular cases, profound completion slices are required to make on magnesium/aluminum alloys that would require two cuts (harsh and finish) on some other alloy.
How does the heat treatment work for aluminum Die Casting alloys?
Most common die casting alloys, such as aluminum alloys, are not a solution/prefer to heat treating.
Low working temperature maturing medicines are utilized for pressure alleviation or dimensional steadiness.
For the most part, T2 or T5 temper brings about properties that are very like those which may be acquired whenever given a full T6 temper.
Furthermore, based on previous observations, aluminum die casting alloys are not heat-treated;
however, there are heat-treatable alloys available and accessible for structural applications, including AA365.
Die casting isn’t for the most part gas and neither a bend welded nor brazed.
Nonetheless, improvements and upgrades in high uprightness die-casting forms combined with strength alloys can empower the practical and complete welding of a die casting in specific applications.
What are the characteristics of Aluminum Die Casting alloys?
The following are the general characteristics of aluminum die casting alloys and given the numbers from range 1 to 5 where 1 stand for most desirable and 5 stands for least desirable:
General Characteristics;
- Approximately Melting Range (degree F): 945 – 1170
- Resistance to Hot Cracking: 1 – 3
- Die-Filling Capacity: 1 – 3
- Anti-Soldering to the Die: 2 – 3
Product Characteristics;
- Pressure Tightness: 1 – 2
- Corrosion Resistance: 1 – 3
- Machining: 3 – 4
- Polishing: 3 – 5
- Electroplating: 1 – 3
- Anodizing (Appearance): 3 – 5
- Anodizing (Protection): 4 – 5
- Strength at Elevated Temperature: 1 – 3
- Resistance to Wear: 1 – 2
These values were judged from experience, and that rating makes comparisons among aluminum die casting alloys only and don’t reflect the relative characteristics of other metal alloys.
What is the Silicon in Aluminum Die Casting alloys?
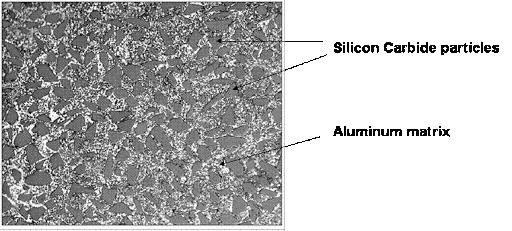
The silicon content in aluminum alloys can approach 11.7%, and one of the most common and preferable aluminum-silicon die casting alloys is AlSi12.
The following are the advantages of these die casting alloys:
- Increase the liquid metal fluidity
- Decrease the solidification shrinkage
-Improves the pressure tightness
-Reduce the hot shortness (tendency to crack or tear during the solidification)
-Increase the modulus of elasticity (Increases stiffness)
-Decreases the specific gravity because silicon is less dense than aluminum
- Decrease the level and intensity the thermal expansion
- Improves the corrosion resistance
Silicon content can be increased above 11.7% to approximately 16.5%, and fluidity and wear resistance can be increase significantly due to the pressure of primary silicon in the die casting alloy.
Furthermore, because of silicons’ high-level of crystalization heat, became the reason of fluidity increment.
However, when the changes occurs in solidifies of silicon, it heats up and release a high-level of this heat and resulting re-heating the remaining amount of liquid aluminum, and becomes the reason for delaying solidification and allows the mass to flow continuedly.
Fluidity contributes to castability but does not help translate directly.
Die casting process parameters, as liquid alloys operating temperatures and micro-cleanliness, die temperatures, and die surface conditions are also improved.
What is the Copper in Aluminum Die Casting alloys?
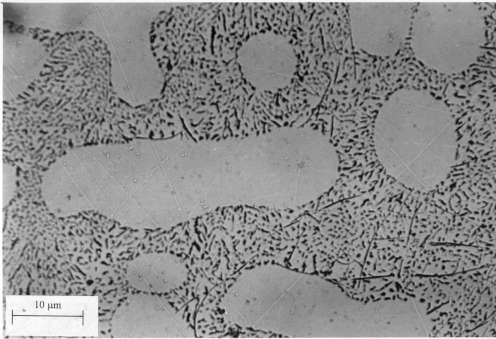
To improve essential and required characteristics, copper has the ability to control its content and in result, it restricted to reduce other elements, environmental/atmospheric corrosion.
The amount of copper mixed up with aluminum is from 2.0% to 3.0%, helps to increase tensile strength and hardness as well as improve the mechanical properties of aluminum die casting alloys at elevated temperatures.
However, in these concentrations, it marginally influences alloy density.
As a fact, that the copper is 3x denser as compared to aluminum.
What are the famous fields of applications of Aluminum Die Casting alloys?
Generally, die casting is used for the vast majority of production series;
i.e., for the majority of components of the same design can be cast, and if the right and suitable die casting alloy are chosen, a high-quality casting is achieved.
The die casting process is particularly suitable for the production of fragile (up to 1 mm) lightweight components, and mostly it depends on the die casting alloy.
Die casting products manufactured/produced for the automotive industry, such as;
- Wheels
- Blocks
- Cylinder heads
- Valve blocks,
- Manifolds
The use of aluminum alloys in die casting leads to a reduction in the weight of the vehicles, and as the outcome of this, reduce the fuel consumption of that vehicle.
Furthermore, there are other top industries in which aluminum die casting parts/products are used:
- Aerospace
- Marine
- Medical
- Automation
- Telecommunication
- Machinery
- Engineering
- Electronics and many others
What is the history of Die Casting alloys?
Die casting got presented in the nineteenth century in the wake of distributing prospered.
The initial aim of die casting was to publish papers quickly, flexibly, and cost-effectively.
Tin alloys are used and got cast into letters; however, when the time passed in 1886 for the first time, it produced the part.
Iron and steel were famous until early 1914.
Because that was the year when a research paper about the die casting alloys mechanical and physical properties published and proven that the aluminum is the perfect alloy for die casting (not in all cases only for the majority).
A short time later, makers perceived the favorable circumstances and advantages of die casting, which could be financially used to deliver parts identified with each field.
Since the twentieth century, die casting innovation has advanced with speeding up.
Around 1914, work started on aluminum alloys, which offered higher qualities.
Copper and magnesium alloys were included in the 1930s.
What to consider when selecting a Die Casting Material?
When selecting the right die casting material for your production, consider taking a look at the following factors:
- The melting point of the die casting alloy
- The general and yield strength of the die casting alloy
- The purity percentage and the level of density of the die casting alloys
- The production and process cost associated with the die casting alloy
- The level of corrosion resistance of the die casting alloy
The selected alloy can influence the die design, the tooling, and the machines employed in the die casting process.
What are the casting characteristics of die casting alloys?
According to a research program investigating the die casting alloys characteristics, it was found that;
The Fe and Mn contents of the alloys are low, and caution has to be taken against the possible die soldering.
At the point when the alloy has a high slop factor, generally, aluminum die-casting alloy, especially an elevated level of Fe, measures must be taken to forestall the arrangement of huge hard spots.
For the casting alloys like aluminum, the Fe substance should keep at its most minimal available level, and the Mn substance ought to be at its most elevated conceivable level.
As far as to alloys science, the components that structure high working temperatures mixes must be kept at their most minimal open level.
The casting alloys ought not to have machining issues when suitable machining methods and machining parameters are utilized.




